Conversion of greek lignocellulosic BiOmass to FURan-based monomers through chemoenzymatic routes
BiO-FURious
Funded by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (H.F.R.I.) under the “3rd Call for H.F.R.I. Research Projects to support Post-Doctoral Researchers” (Project Number: 7315)

About BiO-FURious
From sugars to furans
The BiO-FURious project aims to valorize lignocellulosic biomass wastes and by-products from the Greek agricultural sector towards the production of furan-based monomers that can be used as building blocks for the sustainable production of biobased polymers.
Key points
- Paving the way to obtain valuable products from cheap, abundant, currently utilized agricultural lignocellulosic residues
- Promoting the biorefineries of the present and the future through valorization of side streams
- Setting biocatalysis in the core of green, environmentally – friendly transformation processes
- Replacing petrochemicals with compounds derived from renewable sources – valorizing furans for many applications


Κey players
Lignocellulosic Biomass
• Lignocellulose is composed of a complex structure of different compounds, in which cellulose, hemicellulose (polymeric carbohydrates) and lignin (an aromatic polymer) are intertwined together. The exact proportions of each fraction can vary depending on the type of the plant cell wall.
• Lignocellulosic residues that are made available from the agricultural sector in Greece, like straw, a by-product of cereal production, are either sold at low prices as animal feed or left in the fields because their market price does not cover the costs of collection, baling, and transportation; this biomass can serve instead as a starting material for many valuable products.
• There is a rapidly growing interest in new technologies that can convert renewable, low-cost biomass into high-value bulk chemicals and materials.


Pretreatment and Fractionation
• An integral key step in all investigated technologies for the valorization of lignocellulosic biomass is the application of an initial pretreatment that will enable efficient fractionation of biomass components and convert raw materials to a form amenable to enzymatic or chemo-catalytic downstream conversion.
• Within the frame of BiO-FURious, an initial pretreatment, such as a microwave-assisted organosolv process, will enable efficient fractionation of biomass components and convert raw materials to a sugar streams rich in pentoses and hexoses that can be further converted to furans.
Biocatalysis for sustainable and selective transformations
• During the last few years, much attention has been given to discovering enzymes that can catalyze the conversion of furans.
• The appeal of enzyme catalysts lies in their ability to selectively transform furans with high reaction speed, no toxic by-products and the reaction is conducted in mild environmental conditions (pH, temperature and pressure).
• Downstream mild biocatalytic functionalization (oxidation, reductive amination, reduction) of the produced furans can generate activated monomers (carboxylic acids, furfulylamines, furan alcohols) that would be difficult to access by traditional synthetic chemistry.
• Such compounds have numerous applications as starting materials in synthesis of biopolymers and pharmaceuticals.
Furans as promising compounds
• Furans are promising building blocks for the synthesis of polymers because of their high chemical versatility and functionality.
• They are renewable biobased compounds since they can be obtained from the dehydration of lignocellulose-derived sugars.
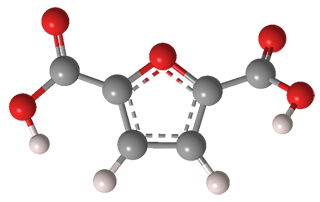
• The 2,5- furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA), produced by oxidation of 5- hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) is a renewable substitute for terephthalic acid for the production of plastics. According to U.S. Department of Energy, FDCA is listed among the top 12 value-added chemicals from biomass nowadays and is considered a highly promising platform chemical with numerous applications.
• The 2-furancarboxylic acid (FCA), produced by oxidation of furfural from furfural possesses significant potential as a monomer in polyester synthesis.
01
Lignocellulose
We foster a culture of innovation, pushing boundaries and exploring new horizons in the realm of biology.
02
Pretreatment
Collaboration is at the heart of Biofurious, where diverse perspectives come together to solve complex biological challenges.
03
Enzymes
Excellence drives everything we do, from our exceptional faculty to our high-achieving students.
04
Furans
Excellence drives everything we do, from our exceptional faculty to our high-achieving students.
